TABLE OF CONTENTS
Importance of Understanding Lifecycle Stages | Lead Status vs Lifecycle Stage | 8 Lifecycle Stages |
Building a Marketing Plan Around Each Stage | Creating Content for Each Stage | FAQs
Generating leads is a top priority for most marketers — that's no surprise to anyone. But defining what a lead truly is and knowing what lifecycle stage each lead is in is even more critical.
Every lead will travel through definable and measurable lead stages with your brand. The message you send to them at each stage determines whether they advance to the next phase of your relationship with them ... or fall through the cracks of a broken pipeline.
Why Is It Important to Understand Lead Lifecycle Stages?
Thinking of the customer lifecycle in these lead stages allows you to track the progress of individuals through your funnel consistently.
When you build a plan around each stage, the individual won’t fall through the cracks and get ignored just because they're not as far along as you thought they would be at this point.
For example, maybe they weren't ready to buy when they first downloaded your Ultimate Guide. If they're a good match otherwise, don't send them back to square one. Keep them in the appropriate stage, and nurture them relative to the progress they've made.
Ideally, nurturing is automated, so this could happen indefinitely if needed. However, as you collect more data, you'll be able to refine your processes so that only leads who've indeed "reached the next stage" get labeled as such.
What's more, you don't waste resources on those who will never progress. Cutting marketing and sales costs over time while increasing your ROI.

Lead Status vs Lifecycle Stage
Lead status and lifecycle stage are two distinct concepts in the realm of customer relationship management and sales. Understanding both concepts is crucial for businesses to tailor their strategies and communication to effectively nurture leads and build lasting customer relationships.
Lead status refers to the current position or stage that a lead occupies in the sales process. It typically includes categories such as:
- New Lead
- Contacted
- Qualified
- Negotiation
- Closed-Won
- Closed-Lost
Lifecycle stage, on the other hand, encompasses a broader perspective, detailing where a contact or customer stands in their overall relationship with a company. It extends beyond the sales process; lifecycle stages cover the entire customer journey, from initial awareness through to becoming a loyal advocate for the brand.
What Are the Different Lead Stages?
Depending on your B2B business model, leads are likely to progress through eight lead stages.

1. Subscriber
You can engage strangers online and keep them returning to your website. But we don't even start measuring lead stages until someone has voluntarily given you some basic information about themselves.
Before this point, most of an unidentified person's activities were hidden due to privacy settings and laws. Until this person reveals themselves, they're just an IP address (if that). You have no control over their experience.
A person enters the subscriber lead stage by following your blog, social activity, or brand. They now consistently see you even if you know little about them.
There's some debate on whether social followers count, so it's important to be clear about your organization's definition. This often comes down to how engaged your followers are.
2. Lead
How many subscribers do you think a SaaS company like HubSpot has? A lot, right?
But not every subscriber is a business buyer or can afford HubSpot technology. Highly engaged subscribers are helpful. They share and comment. They increase social proof. But they may not be leads themselves.
A lead is a person who meets your basic demographic/firmographic criteria to be a potential customer. But lead generation is only the start of the lifecycle stages that carry this lead through becoming a customer.
3. MQL
You now have enough info about this person so that your Marketing team can personalize some of your communications with them. This individual has also demonstrated enough interest in your brand (based on their digital footprint) that Marketing considers them qualified to nurture with more content offers, outreach sequences, etc.
The precise criteria vary by company. A lead becomes a marketing-qualified lead (MQL) when a person who meets basic criteria takes an action like:
- Downloading a guide, case studies, or other lead magnet content
- Taking a quiz
- Downloading multiple offerings
- Attending a webinar
- Watching a video
In other words, you've established that they're worth the extra time and resources it takes to move them deeper into your sales funnel. Typically, after a person becomes an MQL, you pass them to your Sales team for evaluation.
4. SQL
The lead stages continue as Sales evaluates the MQL. If Sales accepts the MQL, the individual becomes a sales-qualified lead (SQL). At this point, Sales will reach out directly to the lead, as it's up to them to carry the baton until the deal is closed/won or closed/lost.
If Sales doesn't think the MQL is ready to become SQL, they could kick it back. However, if you have well-aligned Marketing and Sales teams, the percentage of MQLs that become SQLs immediately is high.
If Sales does outreach with no response, they may also kick it back to Marketing. Often, this is just a matter of timing for the lead, so Marketing will continue to engage the lead as an MQL until they take another action that advances them.
This sounds like a lot of back and forth, and it can be. But lead management automation makes this seamless.
5. Opportunities
If the outreach outcome is favorable, Sales has a hot lead. They'll stay in contact with this person because they’re ready to buy. Sales just need to work out the details, manage objections, and make sure the customer ends up with features that will delight them.
6. Customer
Lead stages don't stop when you make the sale. Instead, onboarding, troubleshooting content, and customer support become vital. You're focused on ensuring the customer can see and experience the value of what they've purchased.
7. Evangelist
A customer who is highly delighted with you will tell others about you, generating word-of-mouth referrals and growth.
This becomes social proof. It magnetizes your brand among your target audience and builds instant trust with new strangers. It expands your reach and drives the lead stages forward faster, shortening the sales cycle.
8. Other
Some leads don't fit into neat packages. These could include job applicants, vendors, employees, and competitors whose contact information you have because they're spying on you. It's common.
How to Build a Marketing Plan Around Each Lifecycle Stage
Your lead stages should align with the inbound marketing buyer's journey. Together, these influence your business’s marketing plan.
- Subscribers are in the Awareness Stage.
- Leads and MQL are in the Consideration Stage.
- SQL and Opportunities are in the Decision Stage.
- Customers and Evangelists are in the Delighted Customer Stage.
What do ideal customers in each stage need to see to move into the next phase with you? This is what you’ll build your marketing plan around. Follow these steps:
- Segment contacts based on where they are in the lead stages.
- Drive endless leads by getting to know your niche audience and what type of content they need at each stage. Set up a system that notifies you when they've entered the next stage (e.g., they download your guide).
- Automate whatever you can to deliver a consistent lead experience.
- Set clear conversion rate goals for each stage and ensure you have the systems and technology to track performance effectively.
- Assess where leads are getting stuck in the pipeline and address it.
- Make note of how quickly people move through stages to forecast the percentage of subscribers who become customers and the revenue it generates. This will become very predictable.
How to Use Marketing Content at Each Stage
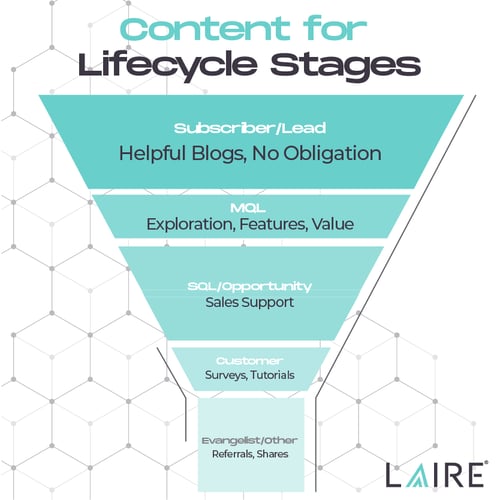
Subscriber Content
This starts with a lead generation website, a site built with a clear goal to generate leads and guide them through the lead stages.
Subscribers need high-quality blog posts that help them explore their problems, why they're happening, and a broad but useful overview of how to fix them. This generates interest in how you help them, capturing more leads.
Think long-term here. How can you build a lasting, meaningful relationship through helpful content?
Position yourself for the long game with the stretch goal of playing a short game. When you do, semi-strangers become invested in a brand without throwing up their defenses before you can connect with them. Think helpfulness first!
Pre-MQL Leads Content
In this lifecycle stage, they know who you are, trust you a little, and will take small actions if you ask them to.
Use calls to action (CTAs) to encourage them to explore your website and learn more. This further positions you as an authority. Ask them to download additional educational content like eBooks, guides, checklists, or whitepapers.
MQL Content
Where interactions may have been casual and sporadic before, an MQL is in the active research phase of its journey.
Selling features in an earlier lifecycle stage would have been confusing, but now leads are ready to hear about the specific features and how becoming a paying customer adds value. Case studies, demos, and free trials help paint this picture.
SQL Content
Now the lead is in Sales. Marketing has less to do with how the lead progresses, but their job isn’t done yet. Marketing can create sales enablement content.
Through marketing automation, becoming an MQL can trigger three events:
- A notification goes to Sales management about the ball in their court.
- The lead is directly assigned to an available Sales agent for follow-up.
- An email sequence begins, which includes sales enablement content created by Marketing to aid Sales in closing the deal efficiently.
Opportunities
Sales follows their processes, closing the deal and signing the contract. That's somewhat out of your hands.
Customer Content
Marketing, Sales, and Customer Service collaborate to create chatbots, troubleshooting videos, tutorials, and other content that help customers get the most out of their purchases. Service sends surveys to take the general satisfaction pulse and even specifics about target customer experiences.
Content to Generate Evangelists
Marketing continues to re-engage customers with email, social media, and re-marketing to generate shares, referrals, social proof, renewals, and more subscribers entering the pipeline.
How Tracking KPIs Improves Your Lead Stages
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) helps you hone in on the lead stages that aren't flowing into the next stage as they should.
Maybe you have subscribers but no leads. You have to ask yourself if you're attracting the right people. Perhaps your MQL to SQL conversion rate is low. It's possible Marketing and Sales aren't in agreement about what an SQL looks like. You could be attracting the wrong crowd. Or your content could just not be doing the job of nurturing people to take that next step.

The insights you'll gain from clearly defining KPIs at each lifecycle stage will help you market smarter with less waste. You'll be able to predict revenues, repeat what's working, and scale it to grow your business.
FAQs About Lead Lifecycle Stages
What’s the difference between a lead lifecycle stage and a sales funnel?
While both describe how a contact progresses toward becoming a customer, lifecycle stages track the contact’s relationship with your brand over time, from subscriber to evangelist, whereas the sales funnel focuses only on the buying journey up to the point of sale.
How do I know when a lead moves from MQL to SQL?
An MQL becomes an SQL once your sales team confirms the lead is ready for a direct sales conversation. This usually happens after specific engagement signals, like requesting a demo, scheduling a consultation, or expressing buying intent, meet your predefined qualification criteria.
Can a lead move backward in the lifecycle stages?
Yes. If a lead stops engaging or isn’t ready to buy, Sales can return them to Marketing for additional nurturing. With clear communication and automation rules in your CRM (like HubSpot), this transition is seamless and keeps the contact in the right stage.
How can I improve my MQL to SQL conversion rate?
Ensure Marketing and Sales share clear qualification criteria, align messaging, and use data-driven scoring. Personalized nurturing and timely outreach also help move leads through the funnel more efficiently.
What kind of content works best for each lifecycle stage?
- Subscribers: Educational blog posts and awareness-level content
- Leads & MQLs: eBooks, webinars, and guides
- SQLs & Opportunities: Product demos, case studies, and ROI tools
- Customers & Evangelists: Tutorials, surveys, and referral programs
How often should I review or update my lifecycle stage definitions?
Revisit your lifecycle stage framework quarterly or when your business model, buyer journey, or CRM setup changes. Regular updates ensure your data remains accurate and your teams stay aligned.
How to Track Lifecycle Stage KPIs
It's no secret that you need certain technologies to track KPIs. Reporting is essential to staying on top of campaign, content, channel, and pipeline performance. It's important to know what KPIs you need to track and how to use technology effectively to track them.
Your tracking and reporting tech stack could include a mix of free and paid tools, like:
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
- Your customer relationship management (CRM) system
- Ad analytics
- Social media analytics
- UTM tracking codes
- Email marketing analytics
If you have questions about tracking KPIs, creating your lead lifecycle stages, or anything else, our team of lead generation pros is here to help. Reach out today, or download our sales enablement guide to keep leads moving through your pipeline.


